Circles
1. Definition & Basics
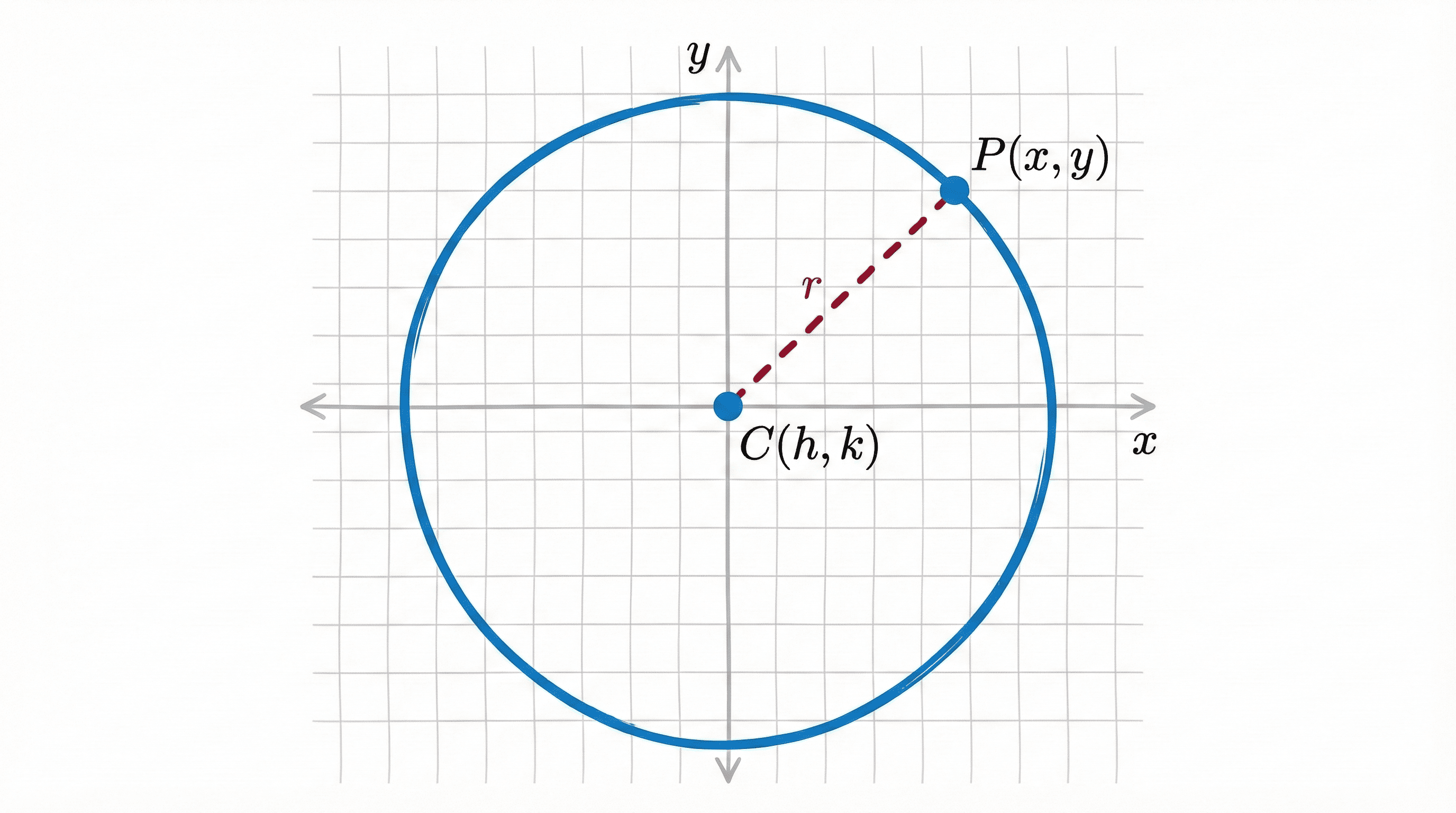
Definition
A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point in the plane.
- Fixed Point: Center ($C$)
- Constant Distance: Radius ($r$)
2. Equations of a Circle
A. Central Form (Standard Form)
If the center of the circle is $(h, k)$ and the radius is $r$:
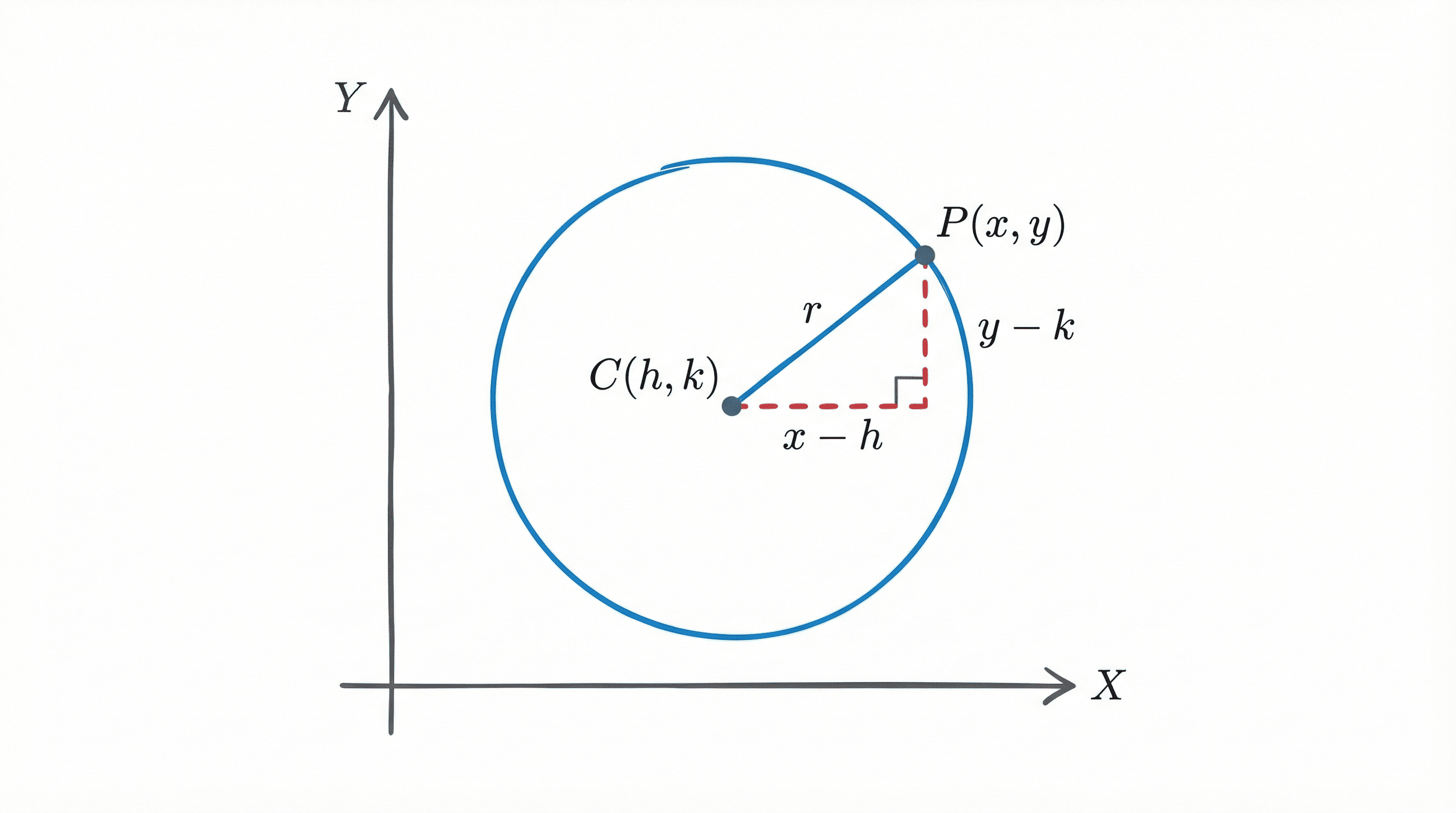
Proof / Derivation
Let $P(x, y)$ be any point on the circle and $C(h, k)$ be the center.
By definition, the distance $CP = r$.
Using the Distance Formula:
$$ \sqrt{(x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2} = r $$Squaring both sides gives the standard equation:
$$ (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 $$B. Simplest Form
If the center is at the origin $(0, 0)$ and radius is $r$, the equation simplifies to:
C. General Equation
The general equation of second degree representing a circle is:
Derivation from Standard Form
Expand the standard equation $(x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2$:
$x^2 - 2hx + h^2 + y^2 - 2ky + k^2 = r^2$
$x^2 + y^2 + (-2h)x + (-2k)y + (h^2 + k^2 - r^2) = 0$
Comparing this with the general form:
- $2g = -2h \Rightarrow h = -g$ (Center x-coordinate)
- $2f = -2k \Rightarrow k = -f$ (Center y-coordinate)
- $c = h^2 + k^2 - r^2$
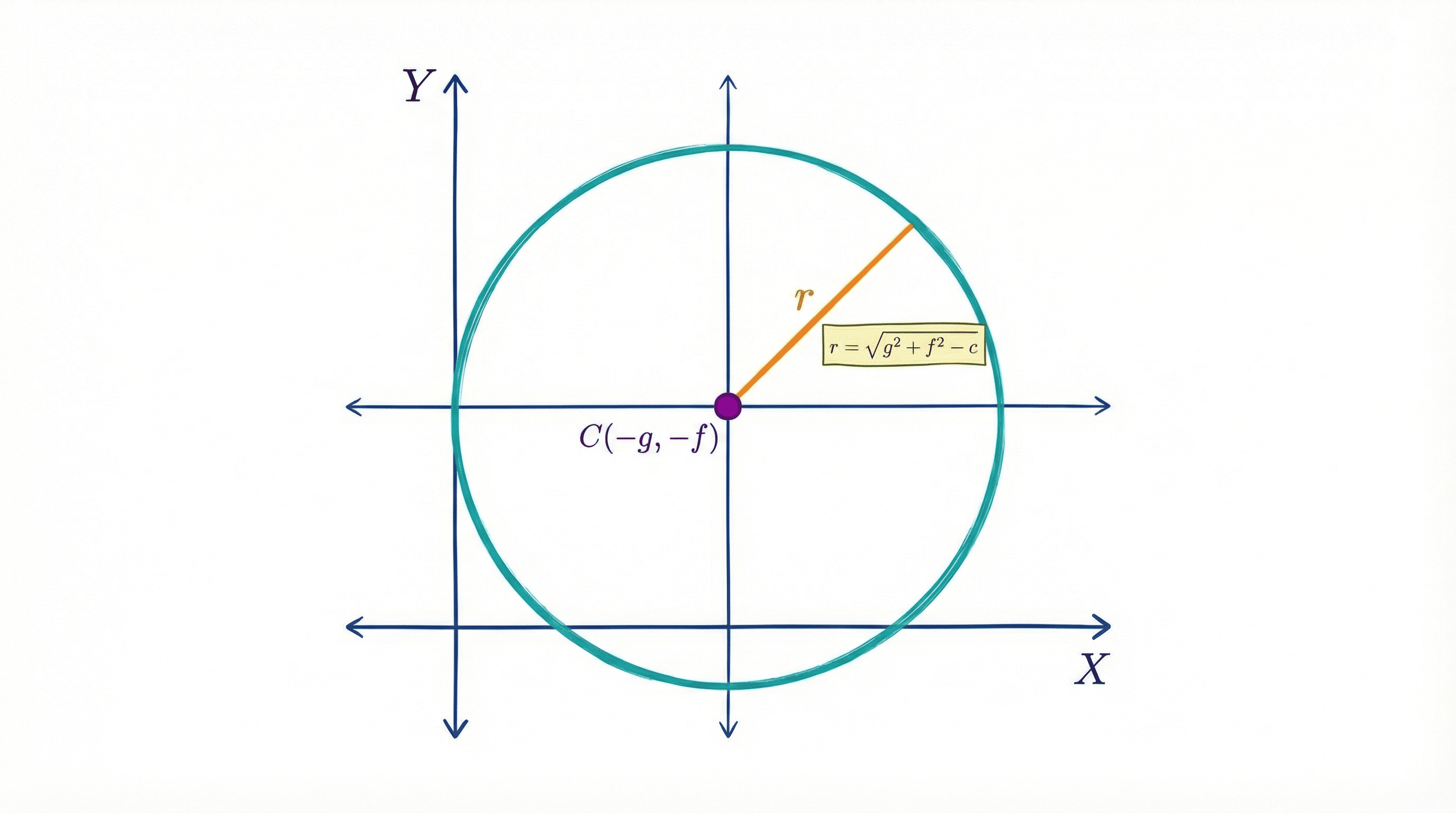
Key Parameters
- Center: $(-g, -f)$
- Radius: $r = \sqrt{g^2 + f^2 - c}$
Nature of Circle
Check the value of $r^2 = g^2 + f^2 - c$:
- $> 0$: Real Circle (Real radius)
- $= 0$: Point Circle (Radius is 0, circle shrinks to a point)
- $< 0$: Imaginary Circle (No real locus exists)
D. Diameter Form
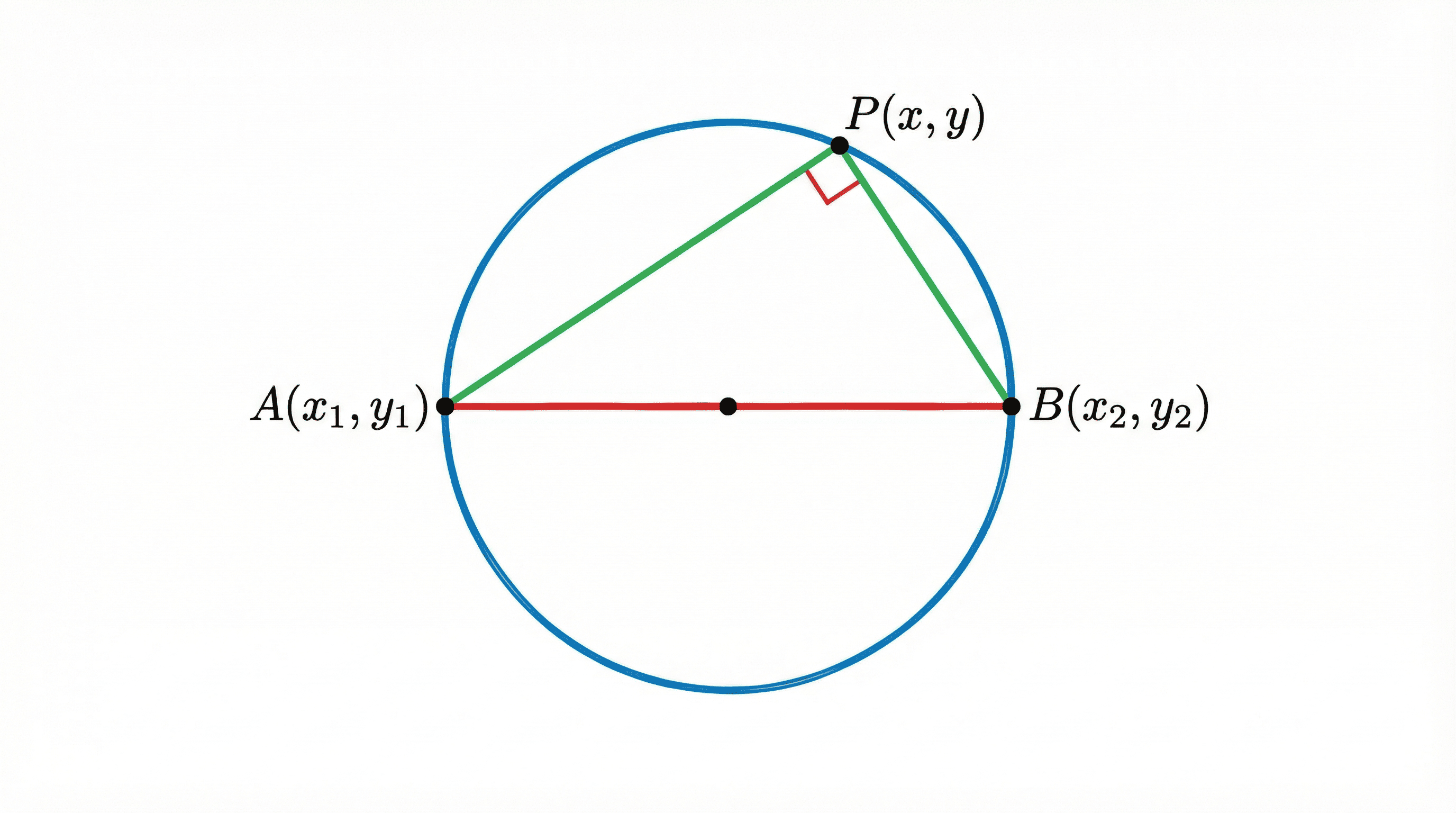
Proof Logic
Angle in a semi-circle is a right angle ($90^\circ$).
Let $P(x, y)$ be any point on the circle. Lines $AP$ and $BP$ are perpendicular.
Product of their slopes $m_1 \times m_2 = -1$:
$$ \left(\frac{y - y_1}{x - x_1}\right) \cdot \left(\frac{y - y_2}{x - x_2}\right) = -1 $$Rearranging terms gives the diameter form equation.
E. Parametric Form
For a circle with center $(h, k)$ and radius $r$, the parametric coordinates are:
where $\theta$ is the parameter ($0 \le \theta < 2\pi$).
3. Geometric Properties
A. Position of a Point
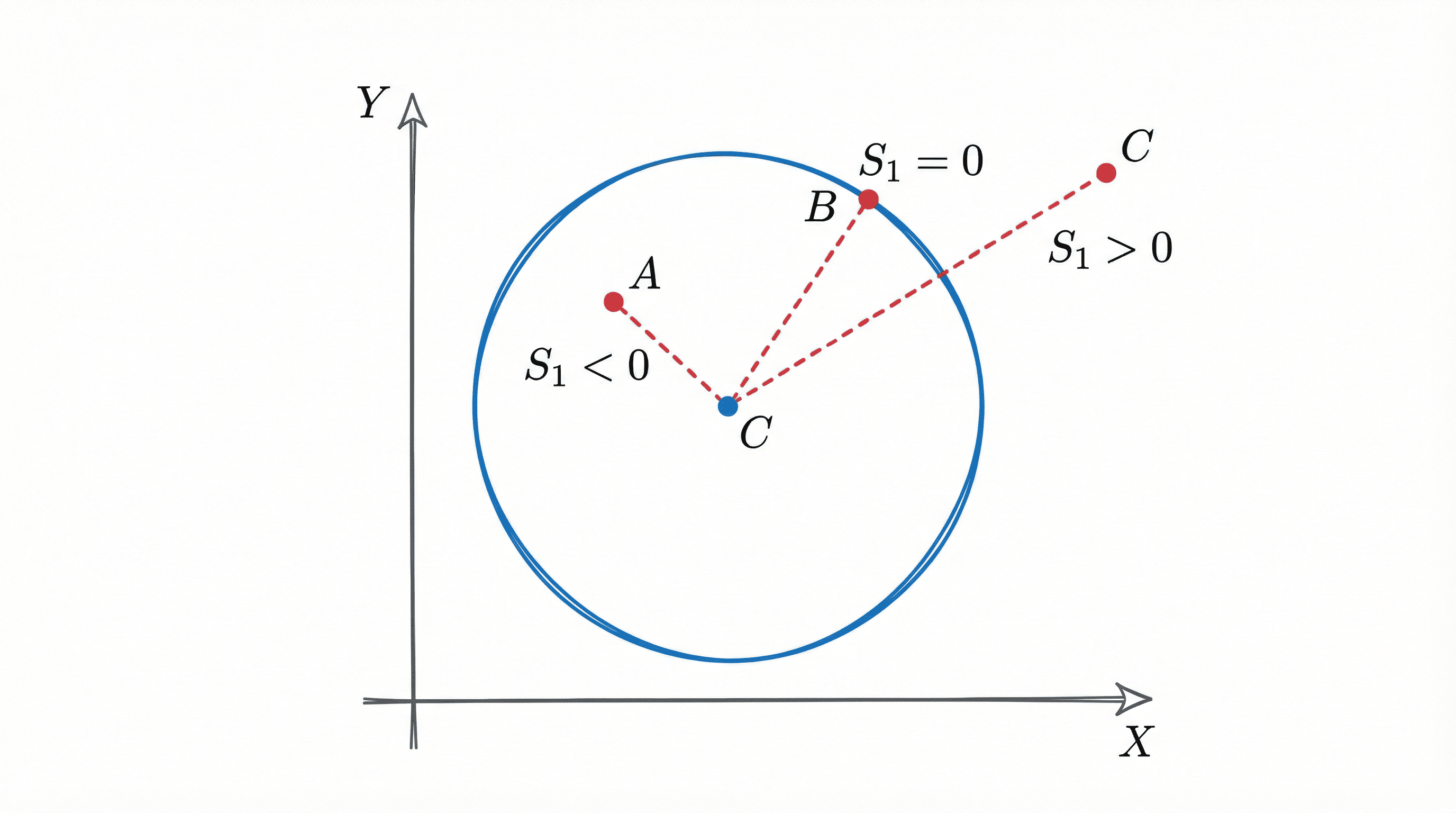
To check where a point $P(x_1, y_1)$ lies with respect to the circle $S \equiv x^2 + y^2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$.
Rule: Power of Point ($S_1$)
Substitute the point coordinates into the equation:
$$ S_1 = x_1^2 + y_1^2 + 2gx_1 + 2fy_1 + c $$- $S_1 > 0 \Rightarrow$ Point is Outside ($CP > Radius$)
- $S_1 = 0 \Rightarrow$ Point is On the circle ($CP = Radius$)
- $S_1 < 0 \Rightarrow$ Point is Inside ($CP < Radius$)
B. Line and Circle Interaction
Let $d$ be the perpendicular distance from the Center to the line, and $r$ be the radius.
- $d > r$: Line does not intersect (No common points).
- $d = r$: Line is a Tangent (Touches at 1 point).
- $d < r$: Line is a Secant (Cuts at 2 points).
C. Intercepts on Axes
If a circle cuts the coordinate axes, the lengths of intercepts are given by:
| Axis | Length Formula | Condition to Cut |
|---|---|---|
| X-Axis | $2\sqrt{g^2 - c}$ | $g^2 > c$ |
| Y-Axis | $2\sqrt{f^2 - c}$ | $f^2 > c$ |
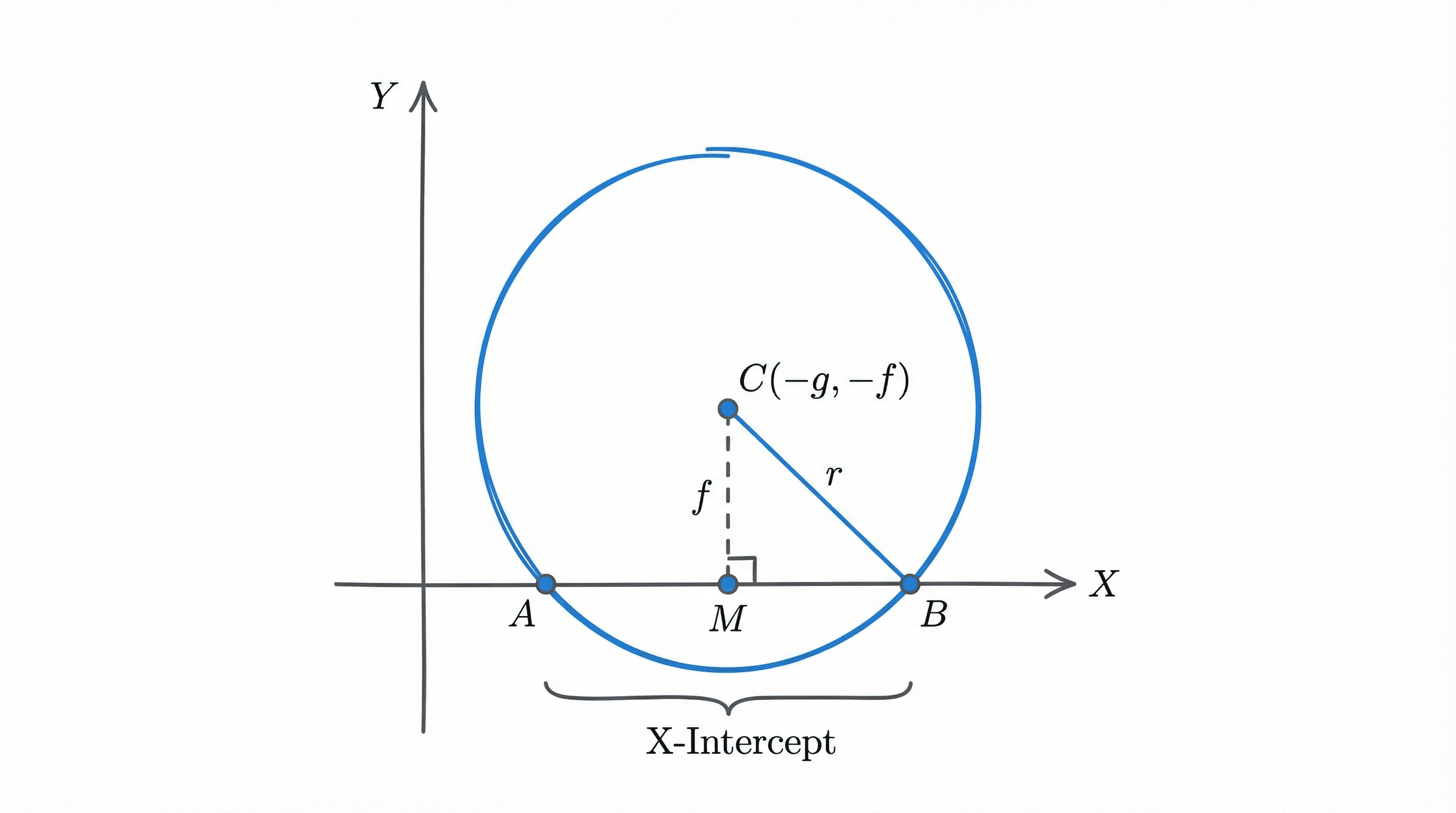
Derivation (X-Intercept)
1. Center $C(-g, -f)$. Perpendicular distance to X-axis is $|-f| = f$.
2. In right $\Delta CMA$ ($M$ is midpoint of chord): $CA = r$, $CM = f$.
3. By Pythagoras: $AM = \sqrt{r^2 - f^2} = \sqrt{(g^2+f^2-c) - f^2} = \sqrt{g^2-c}$.
4. Total intercept $AB = 2 \times AM = 2\sqrt{g^2 - c}$.
Quick Recap
| Form | Equation | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | $(x-h)^2 + (y-k)^2 = r^2$ | Center $(h,k)$, Radius $r$ |
| General | $x^2+y^2+2gx+2fy+c=0$ | $C(-g,-f)$, $r=\sqrt{g^2+f^2-c}$ |
| Diameter | $(x-x_1)(x-x_2) + (y-y_1)(y-y_2) = 0$ | Endpoints $(x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2)$ |